Healthcare
Detect anomalies in ECG signals
The problem: health anomaly detection in ECG signals
Detecting anomalies within human heart ECG signals can help health practitioners identify and diagnose potentially fatal heart conditions to prevent heart attacks or cure heart diseases saving patients’ lives.
The data
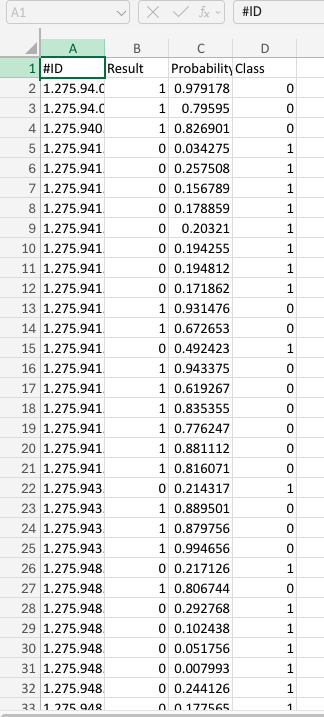
In this use case, we will use a labelled ECG training data to use Butterfly AI platform to detect the ECG anomaly patterns. The data includes samples of ECG time series taken from multiple ECG sensors on human body:
- Each training sample is a sampled ECG signal as a time series
- The last column is the target of the ECG anomaly detection. Label
1indicates the presence of an anomaly and label0means that there is no anomaly - The dataset used is the altered version of the dataset in http://www.timeseriesclassification.com/description.php?Dataset=ECG5000
The base dataset used is (ECGAnomaly.csv).
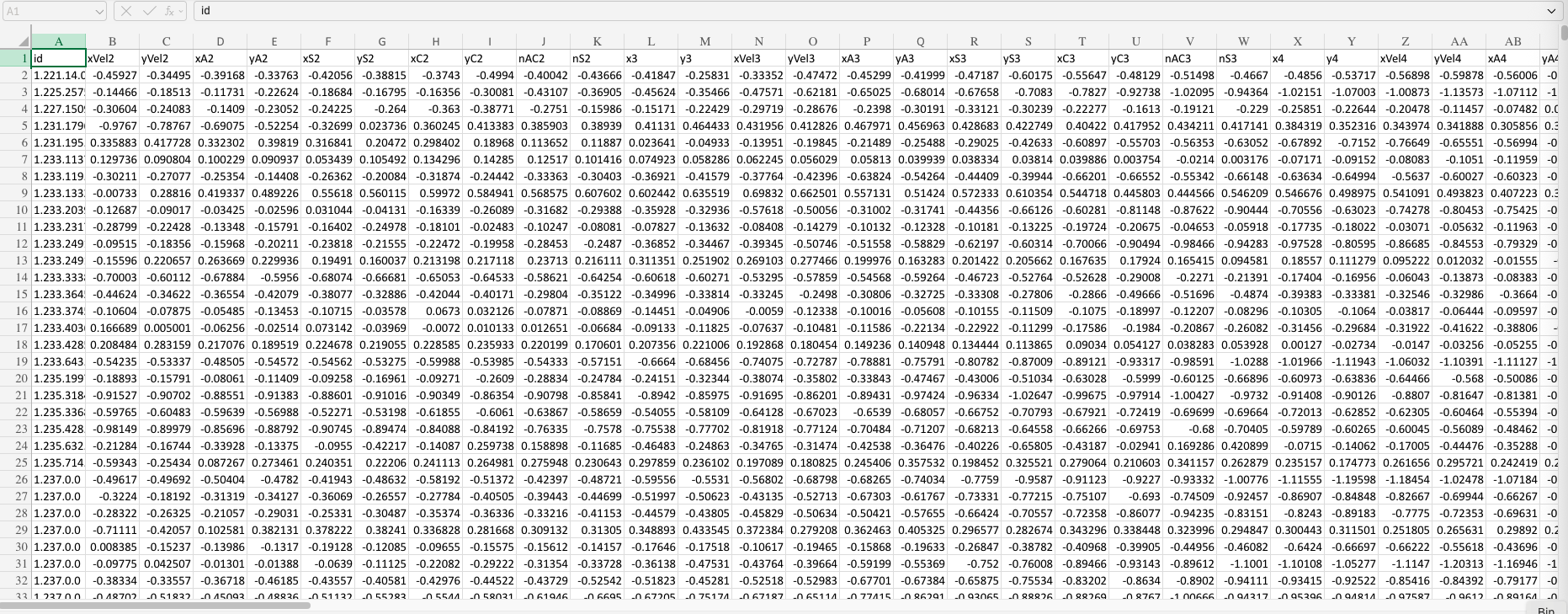
Dataset creation
Use the following parameters for dataset creation:
- number of buckets:
20
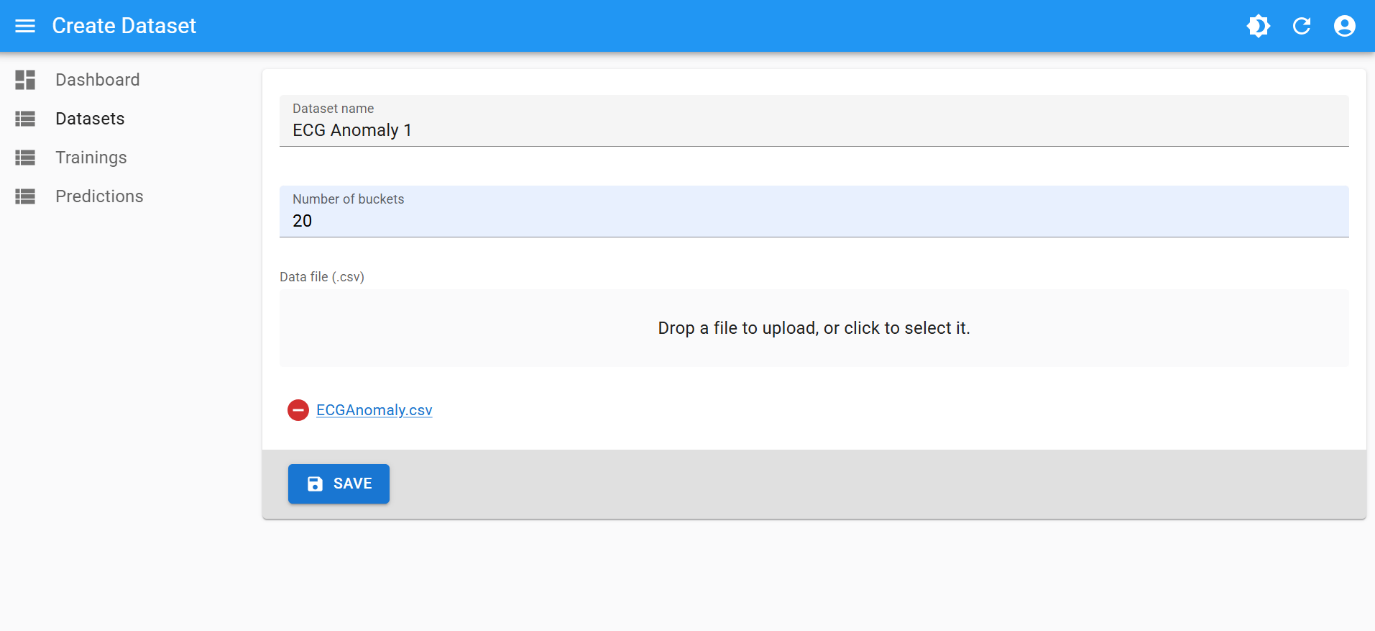
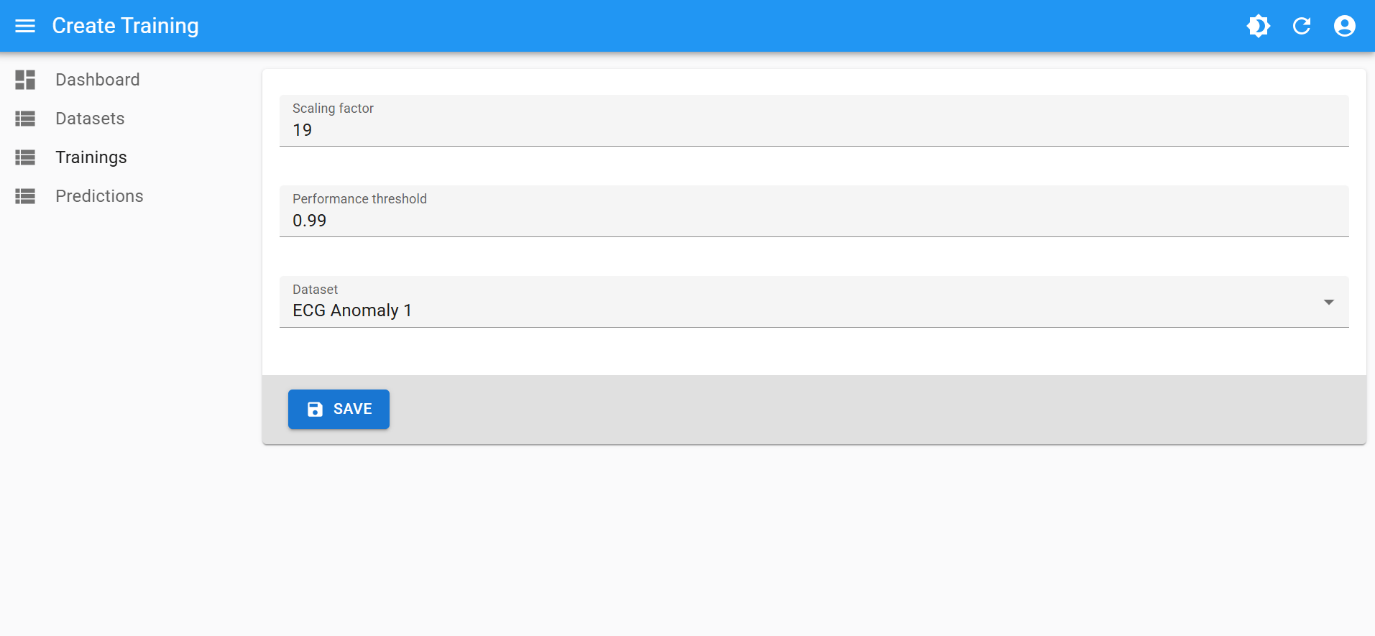
Training
This is the best training attempt:
- scaling factor:
19 - performance threshold:
0.99
And the created champion model:
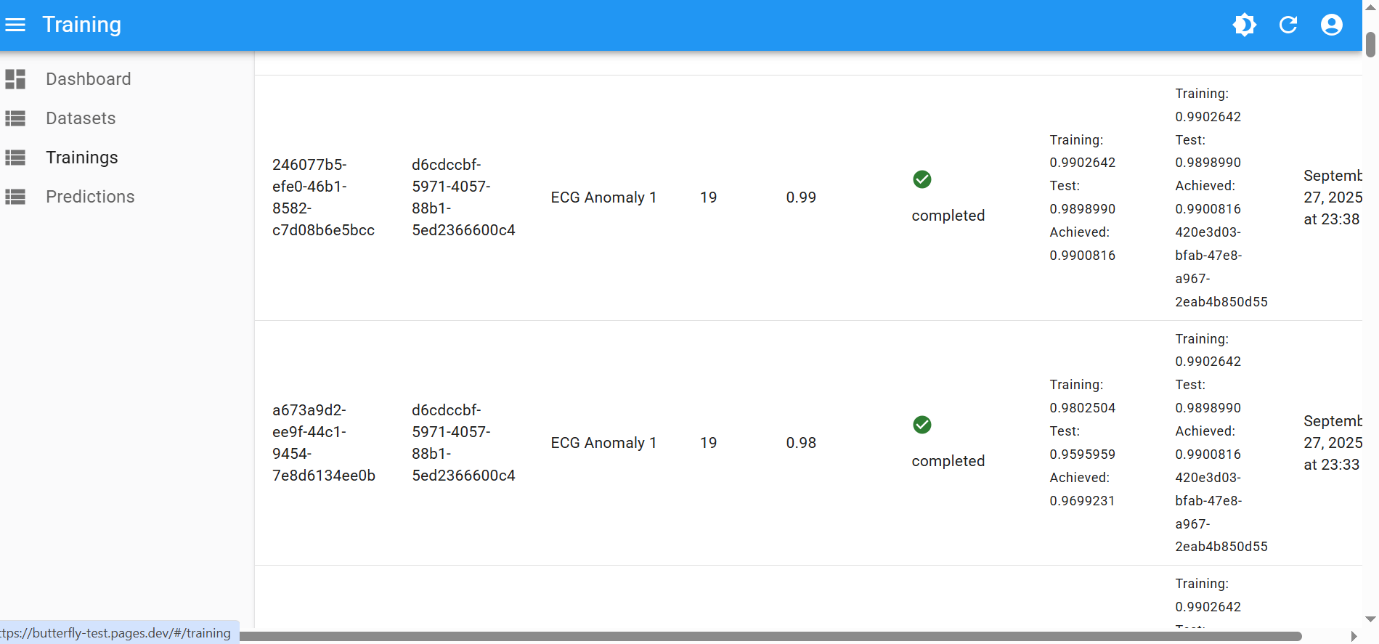
The final performance of 0.99 was achieved after few iterations of hyperparameter tuning:
| Number of Buckets | Scaling Factor | Performance Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| 20 | 19 | 0.80 |
| 20 | 19 | 0.98 |
| 20 | 19 | 0.99 |
Final result
When performing binary classifications or predictions, Butterfly AI platform’s underlying proprietary algorithms calculate the probability of certainty for a prediction outcome.
- One label (e.g.
1) will be selected when the probability is equal or above0.5 - and the other one (e.g.
0) will be selected when the probability is below0.5
The closer the value is to 0 or 1, the more certain is the prediction. The probability is presented in a dedicated column in the prediction result file.
Using this unseen unlabelled data, the resulting CSV looks like this: